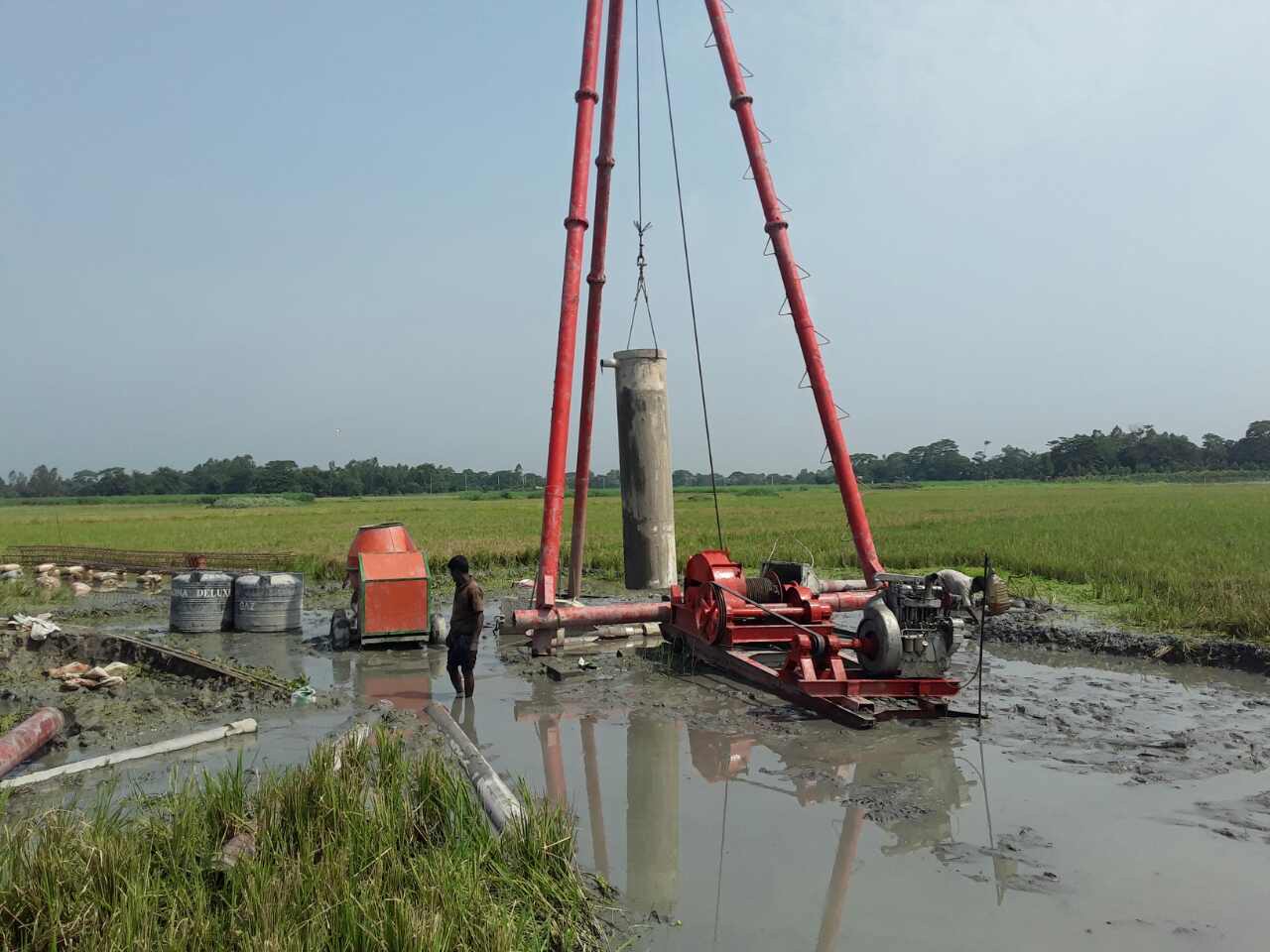

CastinSitu Pile Golden Eagle Networks LTD
Cast in-situ concrete (also termed as cast in-place concrete) is the conventional way of concreting on the construction site. In this the plastic concrete is molded or poured into the formwork, it gets the desired shape on the site and once hardened, it is cured for the required duration. The structural member cannot be brought into the service.

What Is CastInSitu Concrete Cast in Place Concrete Advantages and Disadvantages Concrete
3.Cast-in-Situ Post Tensioned Method. Cat-in-situ Post tensioning method of bridge construction is more demanding method because of its durability and applicability to complex bridge curves etc. In this method along with concrete and reinforcement, steel strands or tendons are also used to introduce post tensioning.
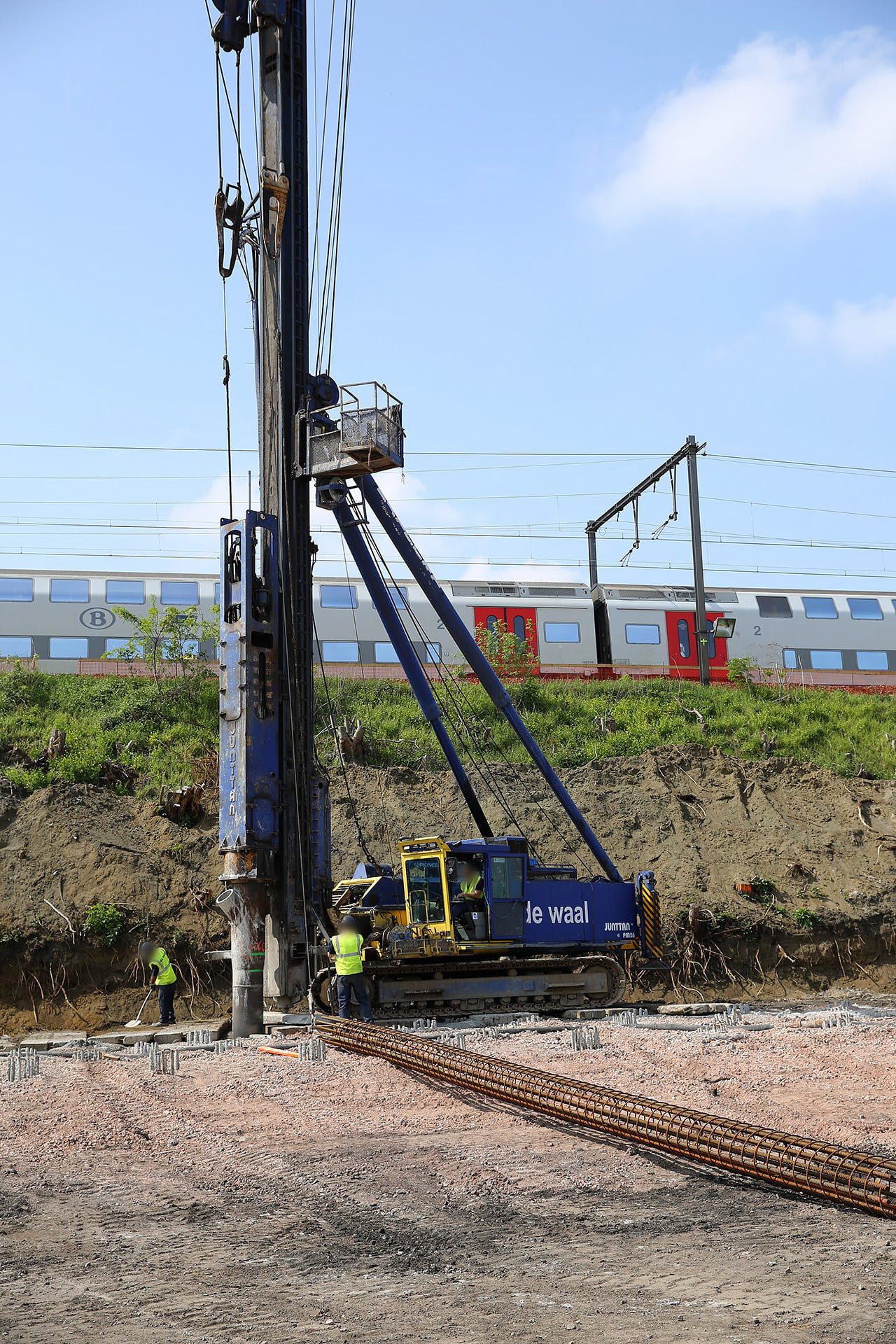

Castinsitu driven piles De Waal Solid Foundations
Practice oriented papers and articles ON CAST IN SITU PILES. In-Situ Properties of Concrete Piles Repaired Under Water. Publication: Concrete International. Date: 3/1/1992. Deterioration of Reinforced Concrete Wharf. Publication: Concrete International. Date: 3/1/1981.
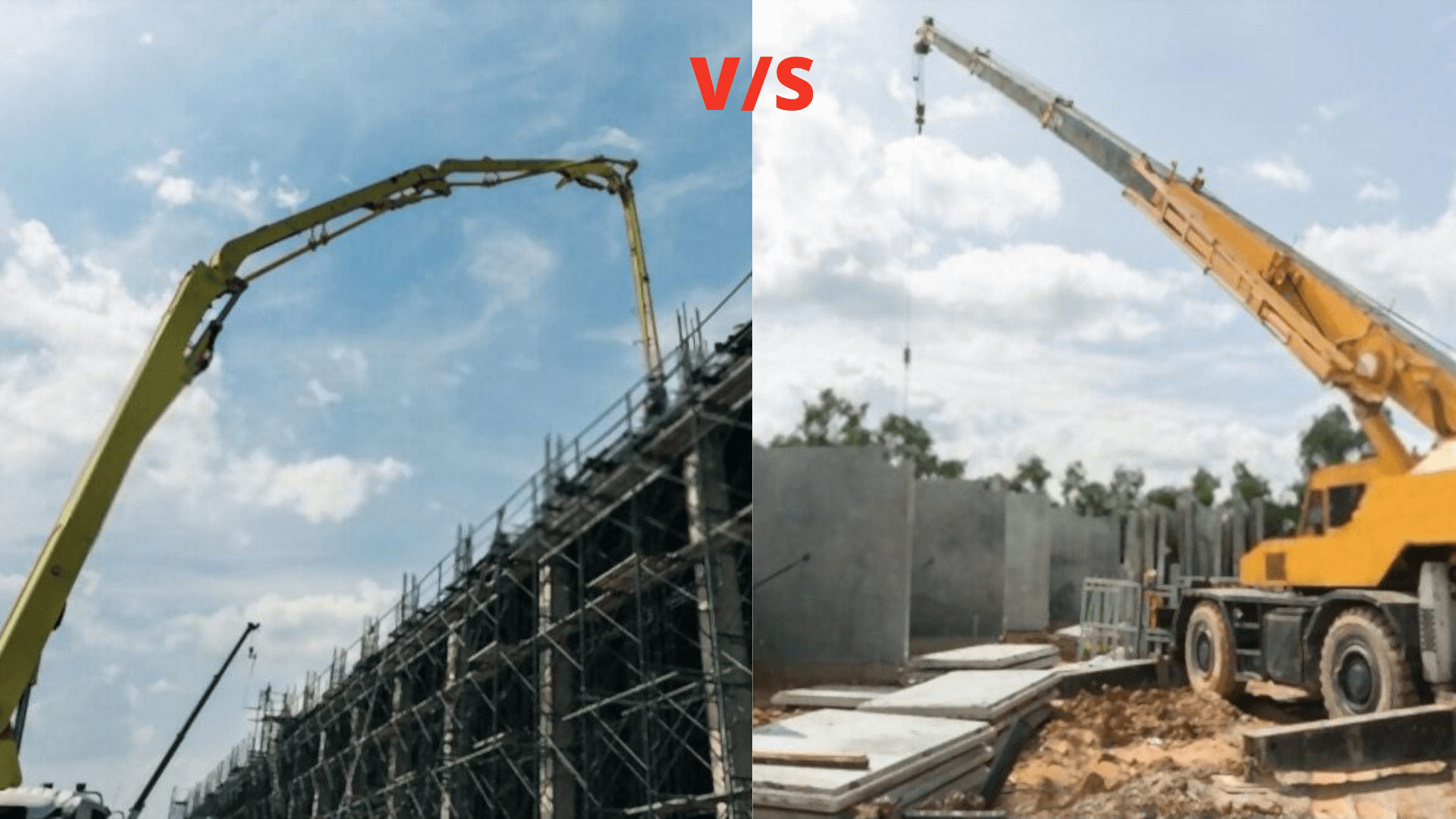
Cast in situ or Precast Concrete! Which one is a Better method Civil Rack
Precast concrete is cheaper for a large construction project, while cast-in-situ concrete is cheaper for a small project like a single house. Why is precast concrete better than cast-in-situ concrete? Precast concrete is better than cast-in-situ concrete for every factor, such as superior quality, lower construction costs, a wider choice of.

Cast in Situ MSM Construction
For example, concrete slabs may be in situ (also "cast-in-place") or prefabricated. In situ techniques are often more labor-intensive, and take longer, but the materials are cheaper, and the work is versatile and adaptable. Prefabricated techniques are usually much quicker, therefore saving money on labour costs, but factory-made parts can be.

RCC Pile concreting cast in situ method YouTube
Precast concrete components are ready for immediate use upon delivery while cast-in-place concrete are not. This eliminates unnecessary time needed to set up cardboard forms, bend and position rebar, pour and vibrate concrete and then wait for the concrete to cure. The removal of these steps saves valuable time in terms of project duration and.

Cast Insitu Kerb and Channel, Slipform TIL
Driven cast in-situ piles are instrumented during the installation process to provide high quality records during the construction process. A robust testing schedule also demonstrates the high performance/quality standards achieved. Driven cast in-situ (DCIS) piles are constructed by driving a closed-ended hollow steel or concrete casing into.
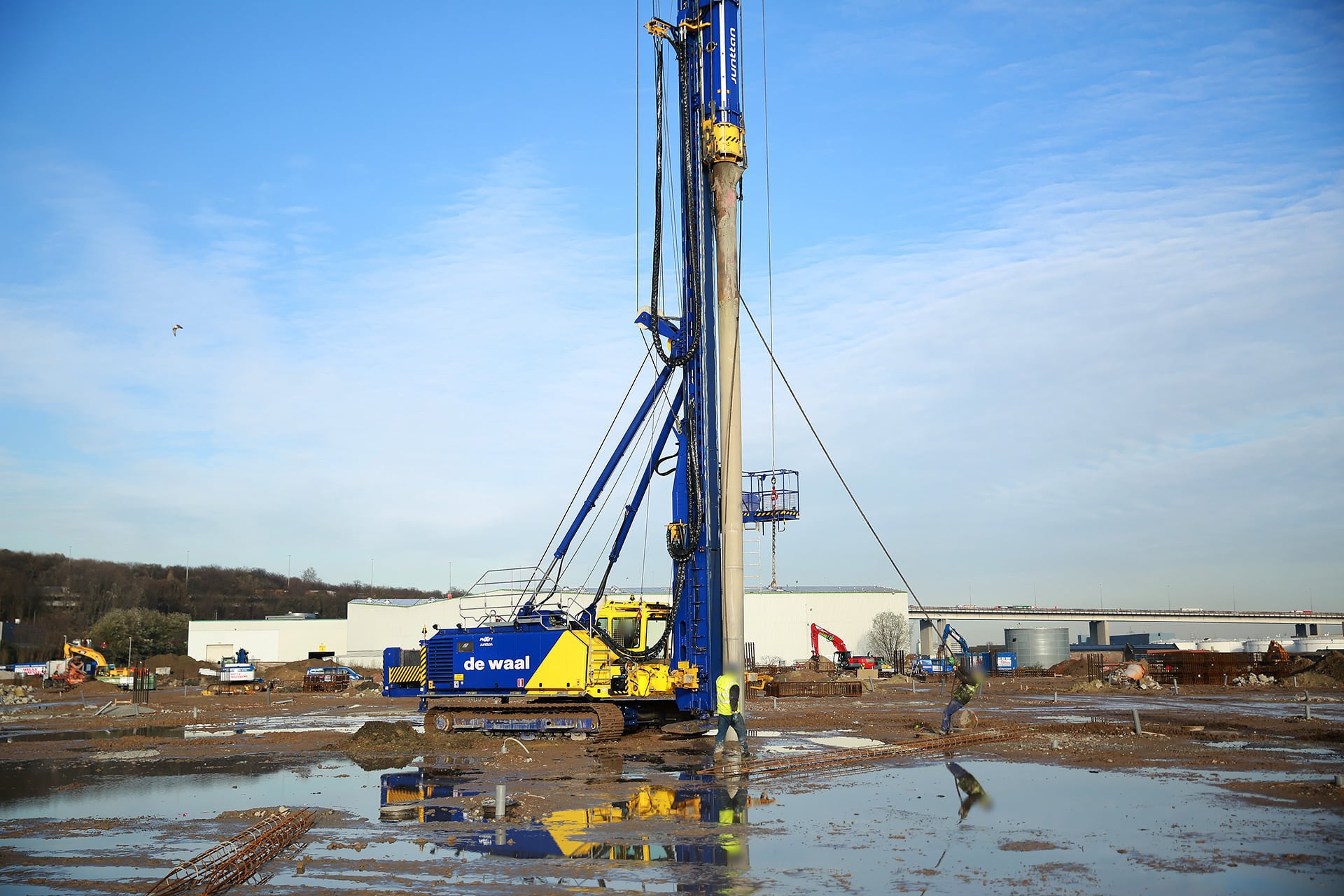

Castinsitu driven piles De Waal Solid Foundations
Cast-in-place Concrete, often known as poured-in-place or cast in situ, is a method of concreting that is carried out in situ, or in the finished location of the concrete component. It is a method of constructing in which the walls and slabs of the buildings are cast on-site in formwork.

1200 mm Bored Cast Insitu piles installation Southern Engineering Co. Ltd (SECO)
WHAT IS SITE CAST CONCRETE? As opposed to precast, site cast, sometimes known as in-situ concrete, is poured, molded and cured on site. Like precast concrete, on site concrete is formed in a mold and then lifted in place. However, one of its advantages over precast slabs is that it does not need to be moved far to be lifted into place.
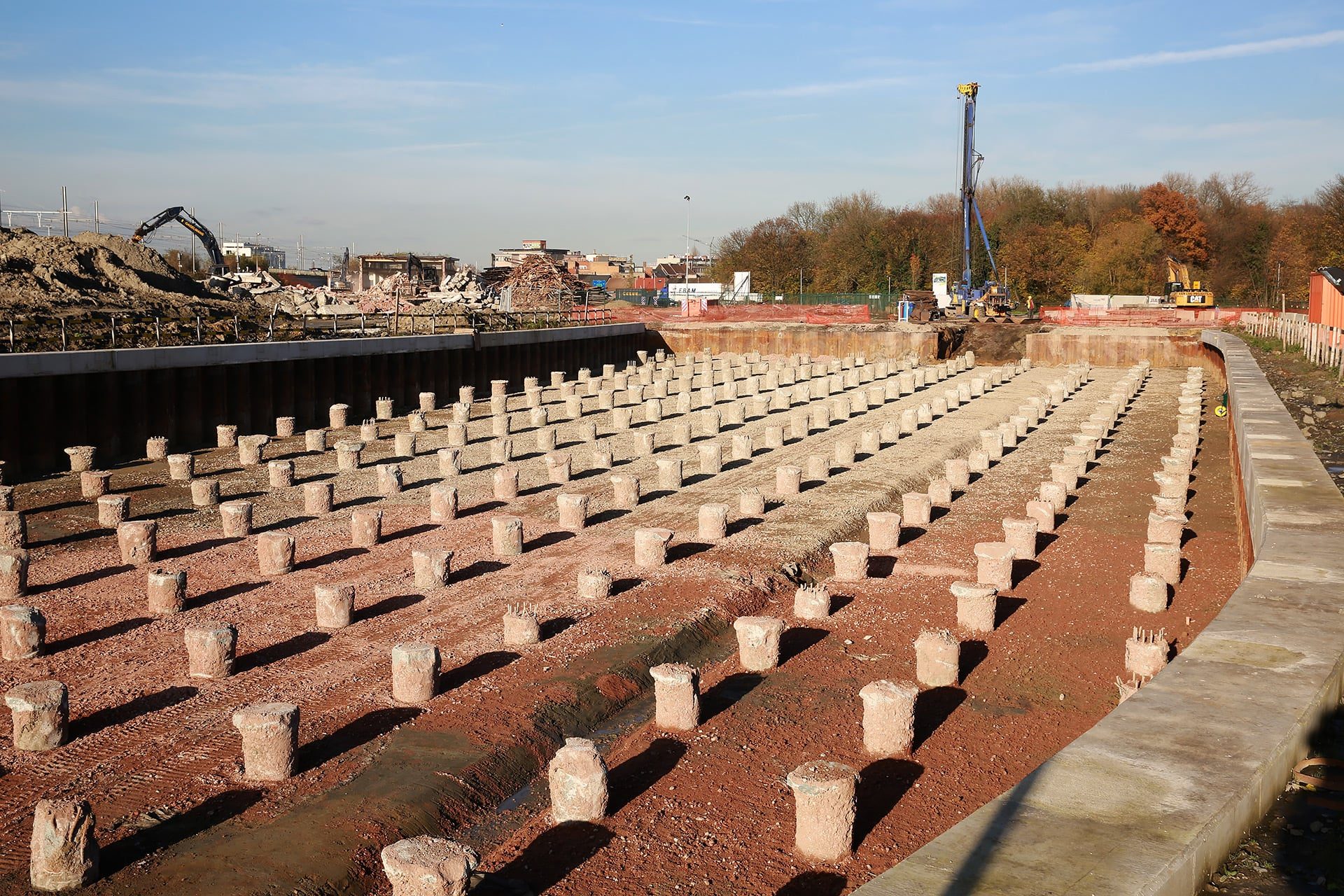

Castinsitu driven piles De Waal Solid Foundations
Cast-In-Place concrete, also known as in-situ concrete, involves pouring wet concrete into forms at the construction site and allowing it to harden in place. This method is often utilized in projects where a high degree of customization and on-site flexibility is required. Cast-in-place concrete is commonly used for building foundations.
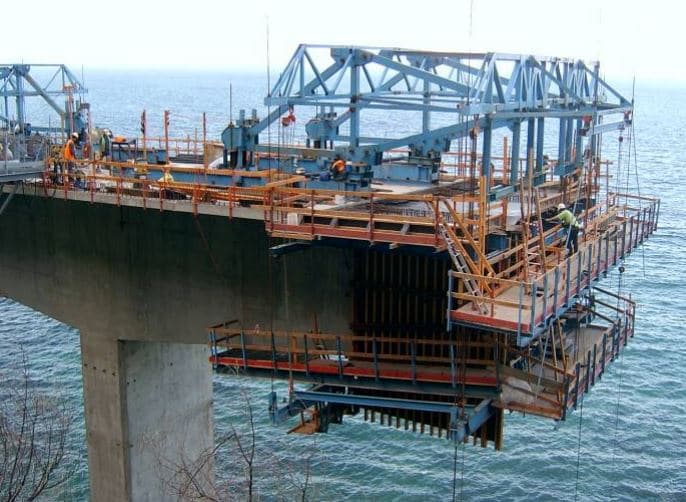

Builtconstruct Different Castinsitu Methods of Bridge Construction
Cast-in-place concrete or Cast-in-situ concrete is a technology of construction of buildings where walls and slabs of the buildings are cast at the site in formwork. This differs from precast concrete technology where slabs are cast elsewhere and then brought to the construction site and assembled.

Cast in Situ MSM Construction
Cast-in-place concrete walls derive their thermal performance characteristics primarily from the amount of insulation placed in the cavity or within the backup wall. Moisture Protection. The most common moisture protection system used with cast-in-place concrete wall systems is a barrier system incorporating an adequate joint seal.

Cast InSitu Lining with EPC's Synthetic Fiber Concrete Reinforcement (1)_web Barchip
Auger cast-in-situ pile is suitable for all kinds of soil and construction sites with limited space. It is vibration free, and a depth of around 18 m can is easily accessible. The diameter of the auger cast-in-situ pile ranges from 40 cm to 100 cm. Figure-4: Auger Cast-In-Situ Pile Displacement Pile Construction

Piling services driven, cast insitu (DCIS) piles Keller UK ESI External Works
Abstract. An essential difference between concrete and other materials used in facade construction is that concrete is poured in place into moulds, or into formwork, rather than being manufactured as a standard size component in a factory. Whereas metal, glass, masonry, plastics and timber are made to standard dimensions in the form of sheets.
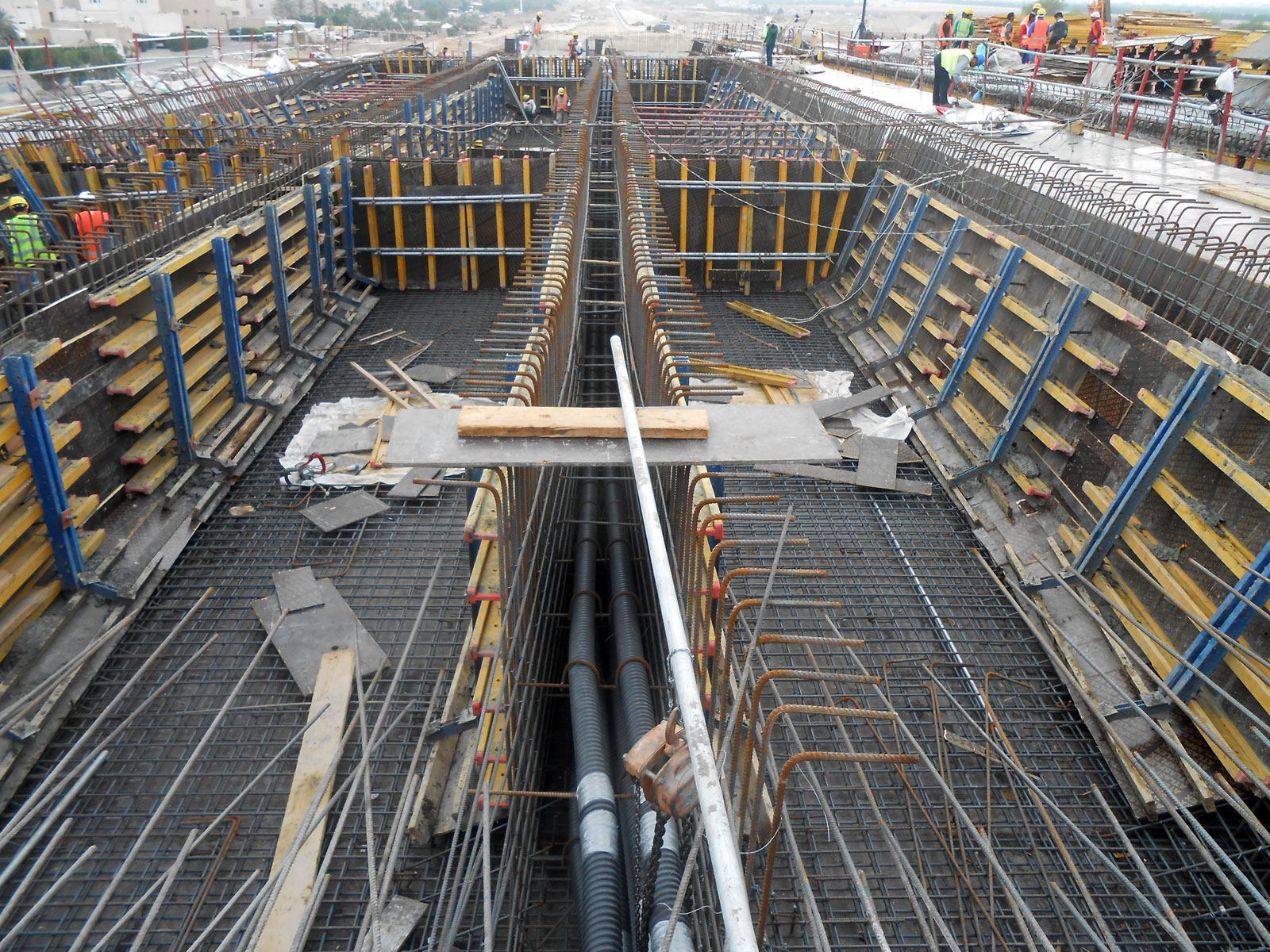

SPAN BY SPAN CAST IN SITU BRIDGE
Cast-in-situ concrete, also known as cast in place meaning, is prepared, placed, and finished on the construction site. This process, often referred to as concrete casting meaning, involves casting of concrete directly where it is required. Generally, concrete slabs, concrete foundations, beam, column, wall, roof, etc., are preferred structures in cast-in-situ concrete.
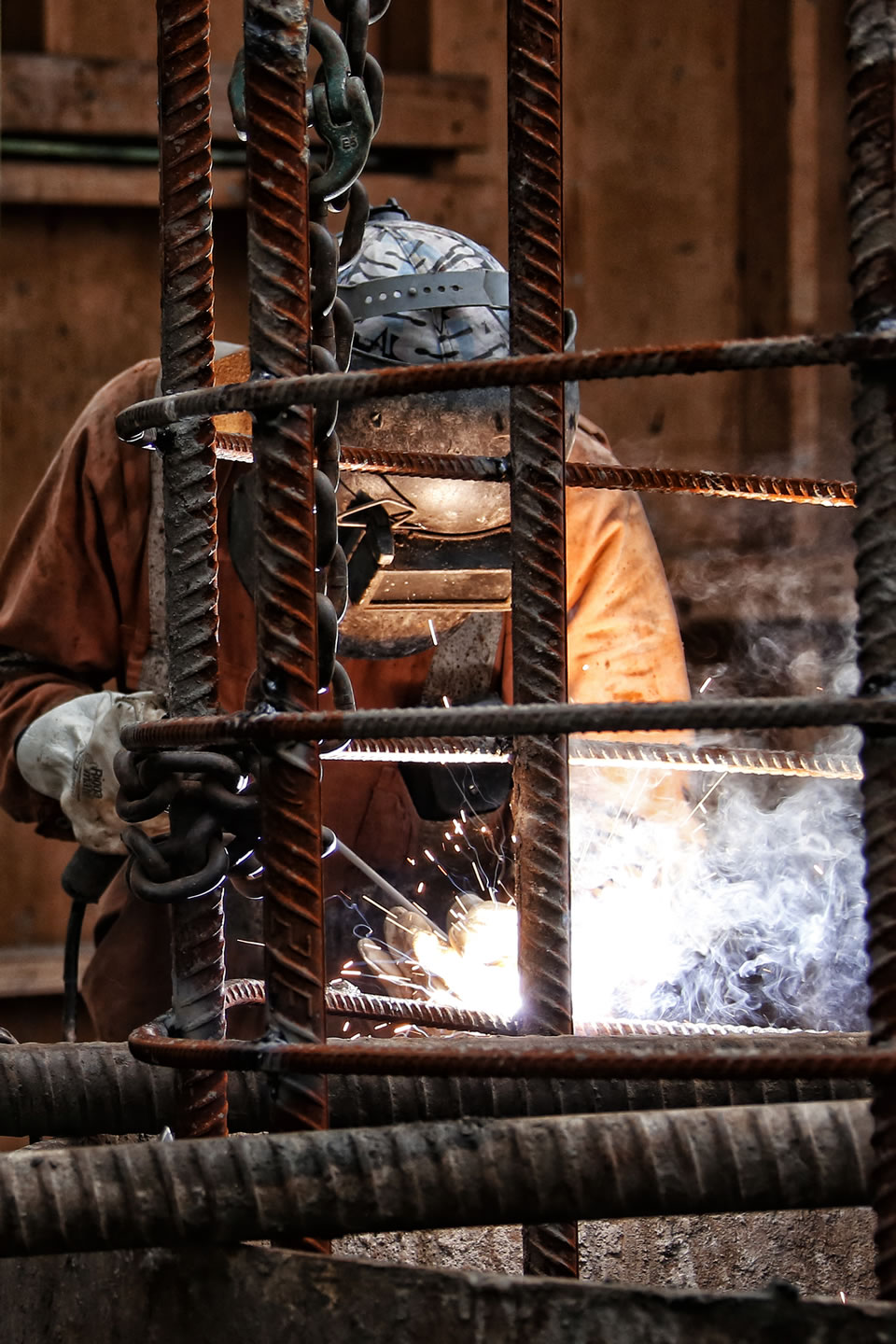

Bored cast in situ
Definition of Cast-in-situ Concrete. The quality of site-cast concrete is also dependent on various factors such as workmanship, how concrete was prepared, parameters of concrete like water-cement ratio, uses of admixtures, type of mixing, etc., Curing process, weather condition, humidity, temperature, etc.